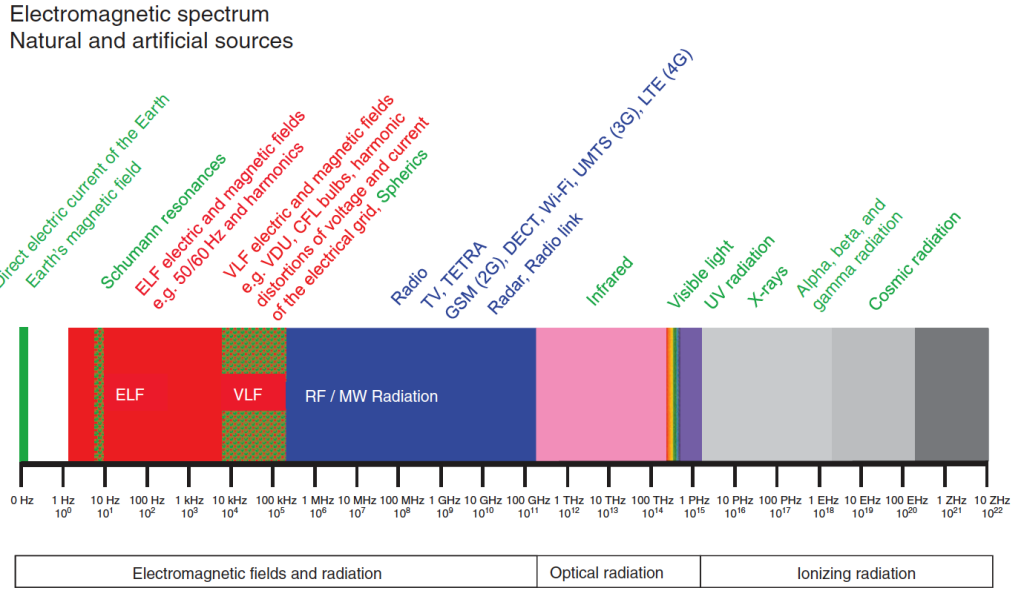
5G – Fifth Generation Cellular Technology
What is it? What are the Heath Implications? How Do You Protect Yourself?
Introduction:
The coming of fifth generation cell technology, known as “5G” has presented modern society with some worrisome aspects. Much has been written about the potential health effects for electrically sensitive and non-sensitive people alike, not to mention animals, insects and our entire biosphere. Concern is mounting. How can we avoid 5G? How can we measure it? How can we protect ourselves from it in our homes and when we go outside in public places? Where are we safe?
WiFi and all of these wireless devices, are themselves potentially harmful to your health and the use of WiFi in public places will be substantially expanded as part of the overall technological evolution that is 5G. Inside your house you have the choice to use WiFi or not, whether to let that 5.8 GHz RF inside your home or not, but in a vibrant urban landscape like Vancouver, BC, you may not be aware of your exposure.
As a Building Biology Environmental Consultants, our goal is to elevate your living or working space to be a healthy, natural environment. We want to help you understand how 4G and 5G work, how to measure it, and how to protect yourselves from the radio frequencies (RF) that 4G and 5G emit. Electromagnetic Fields (EMFs), including RF, are silent, invisible and odourless, so you don’t even know they are there, whether coming in from a 4G/5G small cell antenna outside your home or from a wireless device inside your home, until you measure them. Learn about what is in your home and personal space and follow these three rules: Reduce use, increase distance, and favour hardwired alternatives wherever and whenever possible, including within your home and work space.
What is 5G?
Every ten years or so, the cell industry releases a new generation of technology. For over forty years we have evolved from simple voice service to high-speed audio and HD video data transmissions, where virtually all tasks you could do on a computer can now be done on a handheld device. Communication is virtually instantaneous and many people can’t be without their mobile phone or tablet. 5G is the Fifth Generation of Cellular Technology.
Don’t be confused by the designation “5G” on your router. That is 5.8 GHz, which is a WiFi and cordless telephone frequency (along with 2.4 GHz) used for decades for WiFi and Bluetooth signals transmitted to and from routers, cordless telephones, cell phones, tablets, laptops and many other devices. It is not directly part of fifth generation cellular technology, also known as 5G, although it is peripherally involved as part of the “IoT”, or Internet of Things.
So what does 5G look like?
- It promises lightening fast data download speeds by adding a High or mmWave Band to the existing Low and Mid-range bands.
- These wavelengths are very much shorter and faster and the signal will travel only a few blocks or up to approximately 2.5 square kilometres.
- Because the short wavelengths cannot pass through normal building materials, they will use advanced technologies, including beam-forming, which uses many small antennas (up to 64 transmitting antennas and 64 receiving antennas, and more) that all focus their signal on one or more user’s mobile devices.
- Signals are idle until sent out on-demand when requested by a mmWave 5G-enabled handheld device, unlike 4G which bathes the neighbourhood with strong, always-on radio frequence (RF) energy.
- 5G hand held device (cell phone) must be relatively stationary to stay connected. If it moves, it will likely pick up a 4G signal.
- Primarily an outdoor service.
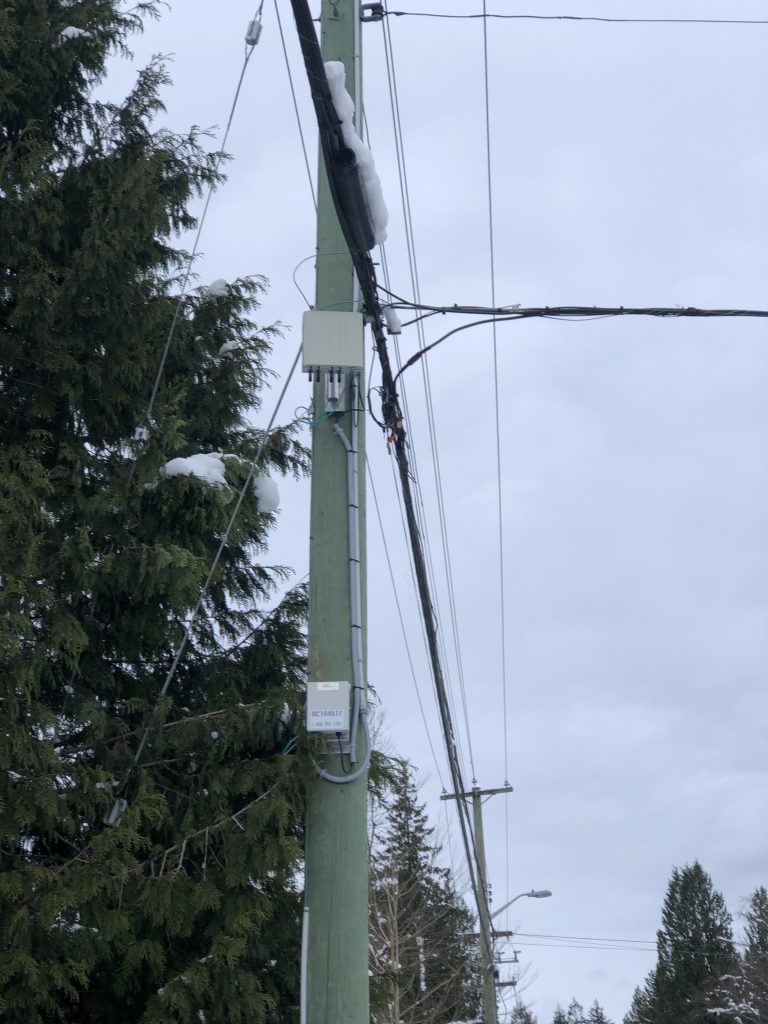
- Antennas will be placed on poles, towers and buildings at existing macro cell sites alongside 1,000 Watt 4G LTE antennas.
- Will also be placed on their own on standalone poles in some neighbourhoods and inside apartment and condo buildings.
- Primarily deployed in dense urban areas and public places: stadiums, arenas, airports, college campuses, and train stations.
- Not expected to be deployed in rural areas any time soon.
- Cannot be measuredwith currently available RF meters.
- Shielding is not easy, only paint, foil, and Aaronia Silver Fabric are expected to be effective.
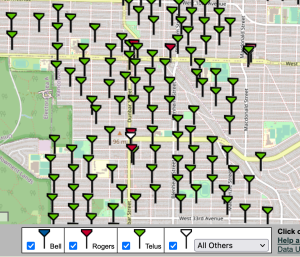 Example of 5G cell sites in Vancouver. Green Flags are the new 5G cell sites
Example of 5G cell sites in Vancouver. Green Flags are the new 5G cell sites
What are the Health Risks of Wireless Transmitters in General?
The wireless transmitters in our mobile devices emit intermittent and now, continuous radio frequency (RF) signals at close range to your body. These signals are silent, invisible and odourless. They can be very harmful on a cellular level, whether we are aware of it or not.
The “International EMF Scientist Appeal” (EMFscientist.org) addresses the concerns of 215 scientists from 40 nations about the adverse health effects on the human population exposed to non-ionizing electromagnetic fields (EMF) from extremely-low frequency to radio frequency. The Appeal has been submitted to the United Nations, to two of its sub-agencies, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP), and to all UN Member Nations. The overall weight of evidence reported is peer-reviewed and scientific studies strongly supports greater precautionary measures be taken to reduce or eliminate EMF exposure. It details numerous recent scientific publications that have shown EMF affects living organisms at levels well below most international and national guidelines. Effects include increased cancer risk, cellular stress, increase in harmful free radicals, genetic damages, structural and functional changes of the reproductive system, learning and memory deficits, neurological disorders, and negative impacts on general well-being in humans. Damage also goes well beyond the human race, as there is growing evidence of harmful effects to both plant and animal life.
Are There Additional Health Risks with 5G?
5G will not replace 4G; it will accompany 4G for the near future and possibly over the long term. Therefore, the potential effects will be cumulative.
What differentiates 4G signal from 5G signal is the amount of modulation and pulsing that occurs in creating and shaping the cell signal. The short wavelength of these signals means they will not penetrate much deeper than the skin, but the skin itself is a large organ with its own integrity and biological properties. Exposure to signals in the mm band may have the potential to harm skin and eyes on a micro level.
How to Protect Yourself:
- 4G and 5G signals can be shielded by various materials, depending upon the frequency of the signal. That is why it is important to know that 5G will come in three frequency ranges. In the low and mid bands, RF-shielding paints, copper mesh, aluminum building foil, window film, and most RF-shielding fabrics are all relatively effective at blocking RF, if you are careful in your analysis and application of the material.
- In the super-20 GHz mm wave high mmWave band, however, only paint and building foil will be effective.
- You can best protect yourself in your own home by not purchasing a 5G-enabled cell phone, keeping cell phones off when at home, and using hardwired alternatives for all your devices.
- Do not bring new 5G-enabled wireless devices into your home, such as new routers and smart speakers.
- Opt out of your electric, water and gas utility’s smart meter programs, if possible. If not, shield your smart utility meters with a smart meter guard.
- Hire a building biologist to measure the RF levels inside and outside your home and help guide you on how to shield effectively and find hardwired alternatives to wireless devices.
5G is happening now, and it is important to take the appropriate steps to protect your space from its harmful impacts. If you have more questions about 5G and how it can impact you and your family, contact us today!